Application & Technical Notes
Request a demo or quoteApplication Notes
3D Cell Explorer 96focus
This Application Note covers how the 3D Cell Explorer 96focus performs high content label free phenotypic screening, showing how this state of the art technology can be used for in vitro preclinical toxicology and de risking studies to increase translational relevance.
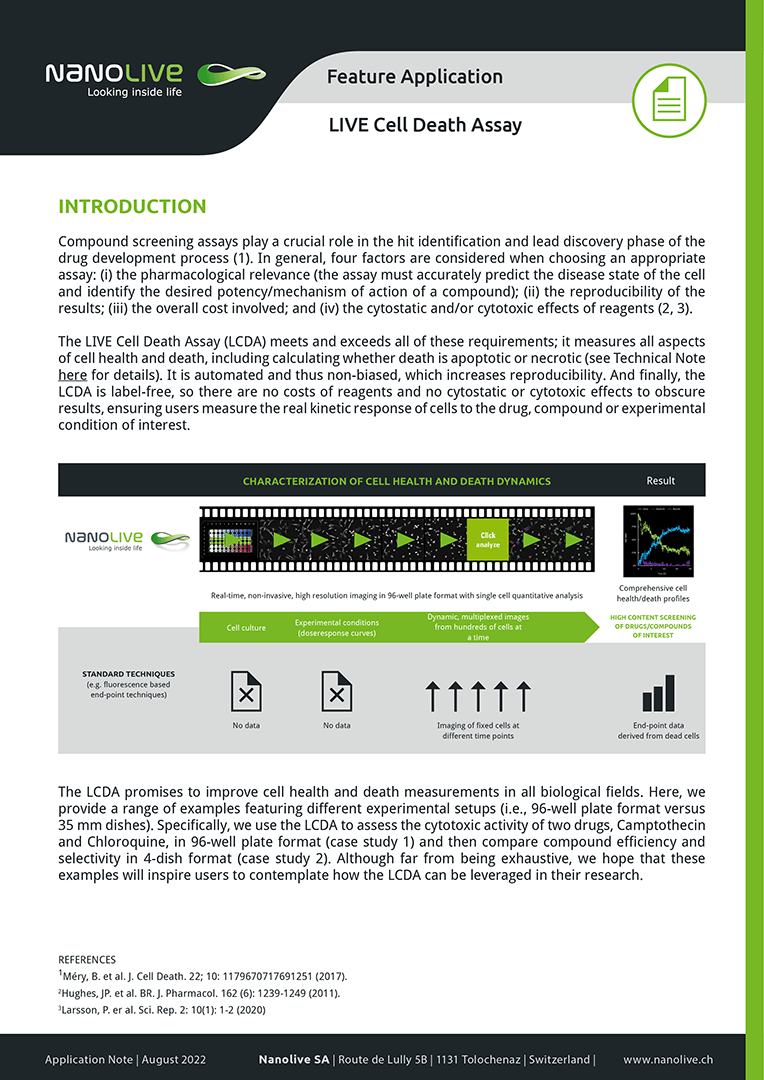
LIVE Cell Death Assay
The LIVE Cell Death Assay (LCDA) provides a unique and complete solution for measuring the phenotypic and cytotoxic activity of compounds, drugs or experimental conditions in an automated and noninvasive(label-free) fashion.
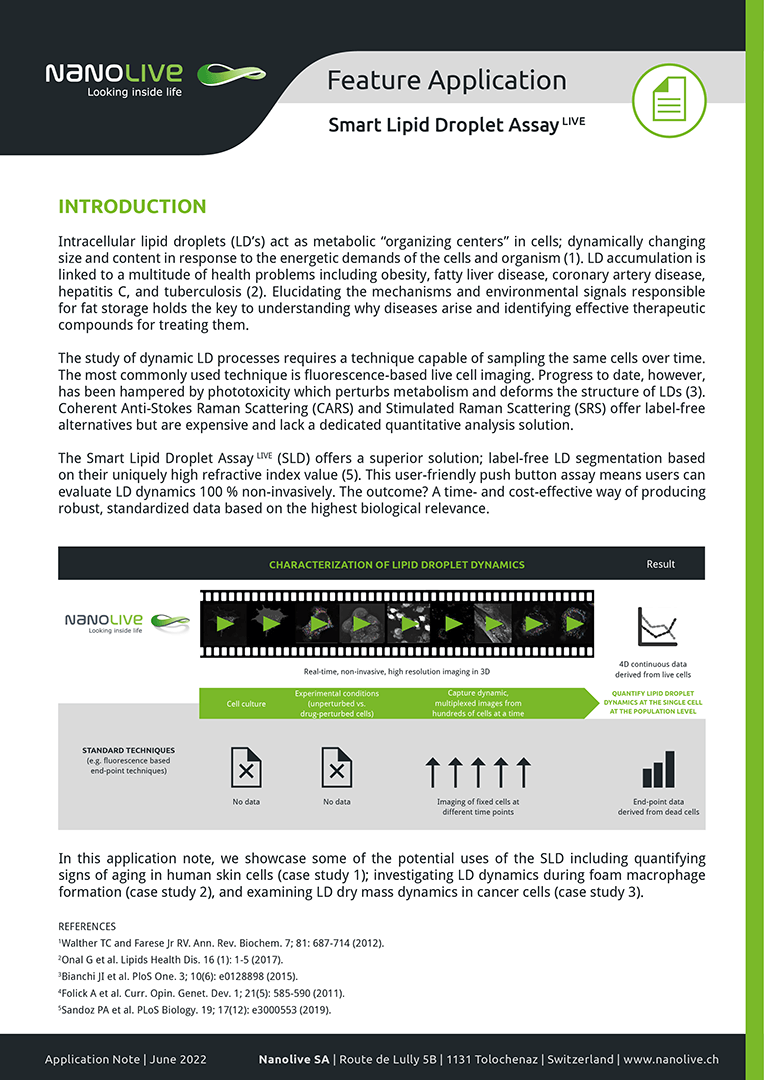
Investigating LD Dynamics
In this application note, we showcase some of the potential uses of the Smart Lipid Droplet Assay (SLDA) including quantifying signs of aging in human skin cells (case study 1); investigating LD dynamics during foam macrophage formation (case study 2); examining LD dry mass dynamics in cancer cells (case study 3), and dissecting the details of LD biogenesis (case study 4).
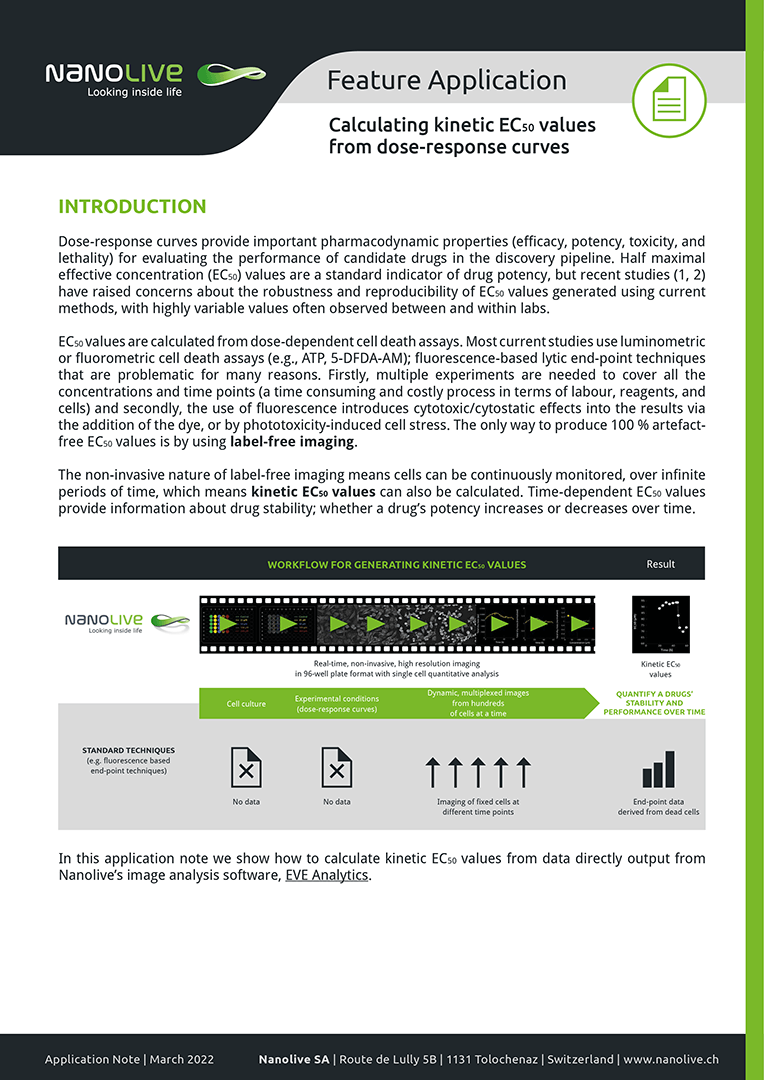
Calculating kinetic EC50 values
The non-invasive nature of label-free imaging means cells can be continuously monitored, over infinite periods of time, which means kinetic EC50 values can also be calculated. Time-dependent EC50 values provide information about drug stability; whether a drug’s potency increases or decreases over time. In this application note we show how to calculate kinetic EC50 values from data directly output from Nanolive’s image analysis software, EVE Analytics.
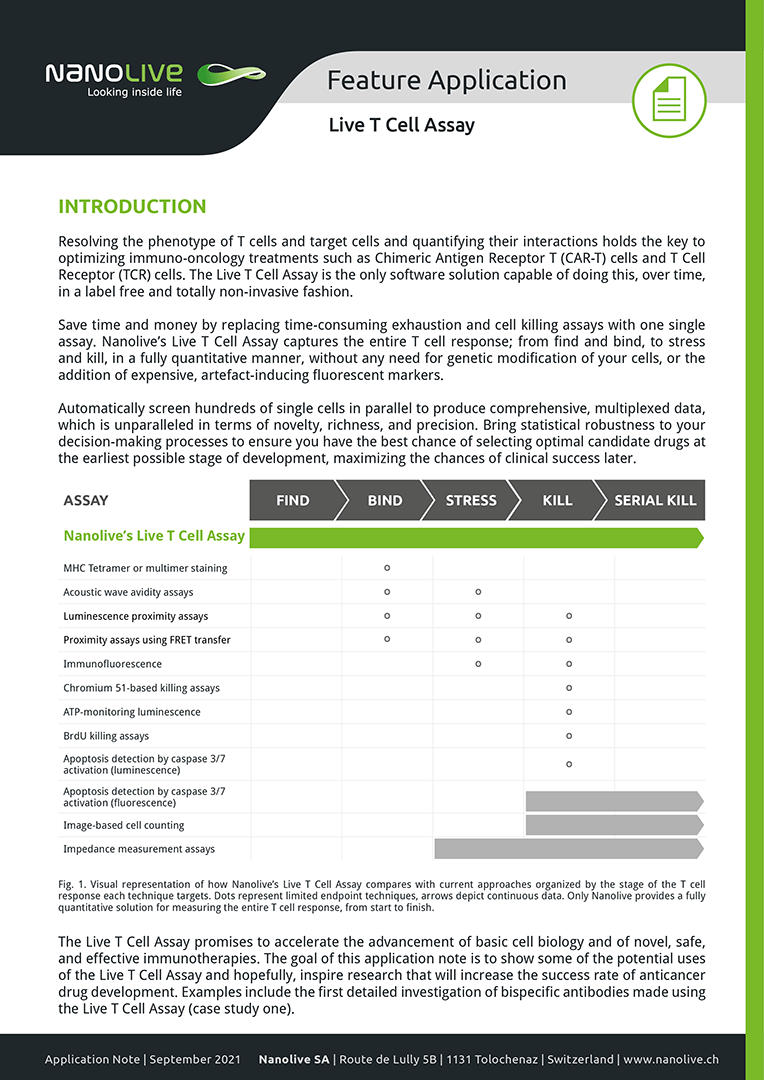
Dissect the entire T cell response
The Live T Cell Assay promises to accelerate the advancement of basic cell biology and of novel, safe, and effective immunotherapies. The goal of this application note is to show some of the potential uses of the Live T Cell Assay and hopefully, inspire research that will increase the success rate of anticancer drug development. To this end, we present the first in-depth investigation of bispecific antibodies using the Live T Cell Assay.
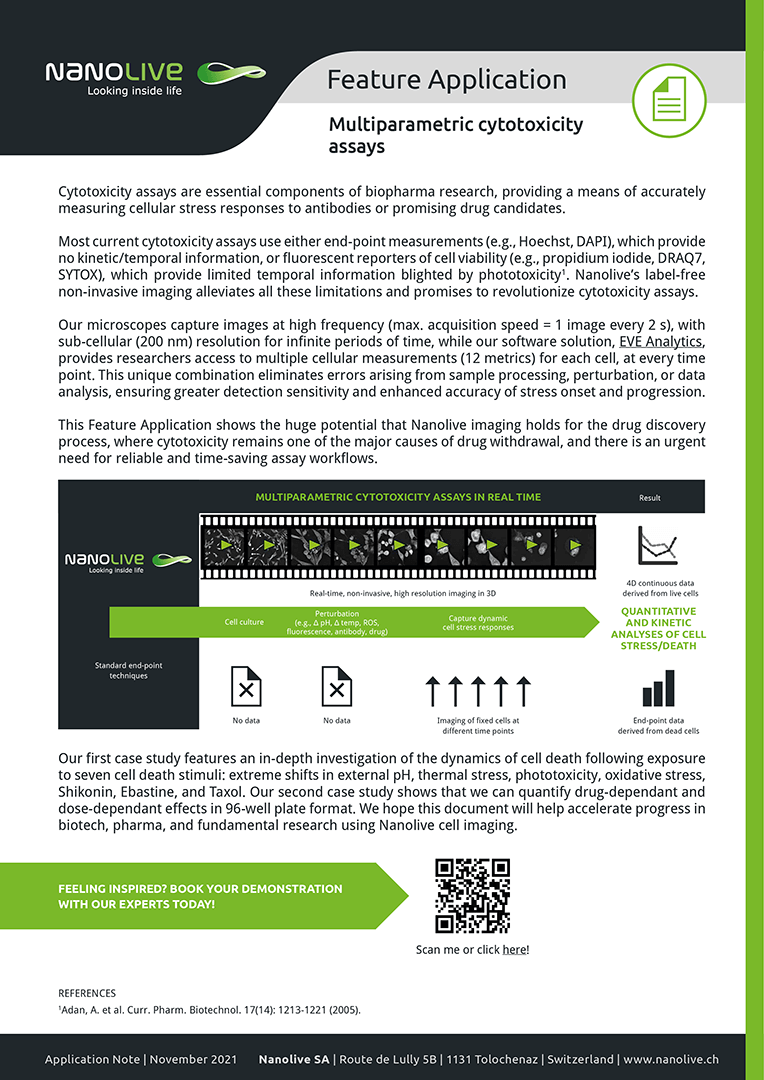
Multiparametric cytotoxicity assays
In this application note we demonstrate how the huge potential that Nanolive imaging holds for the drug discovery process, where cytotoxicity remains one of the major causes of drug withdrawal, and there is an urgent need for reliable and time-saving assay workflows. We show it is possible to quantify the onset and progression of stress with high precision, bringing greater accuracy to cell death research and that different cell death stimuli show unique signatures in cell metrics (case study one).
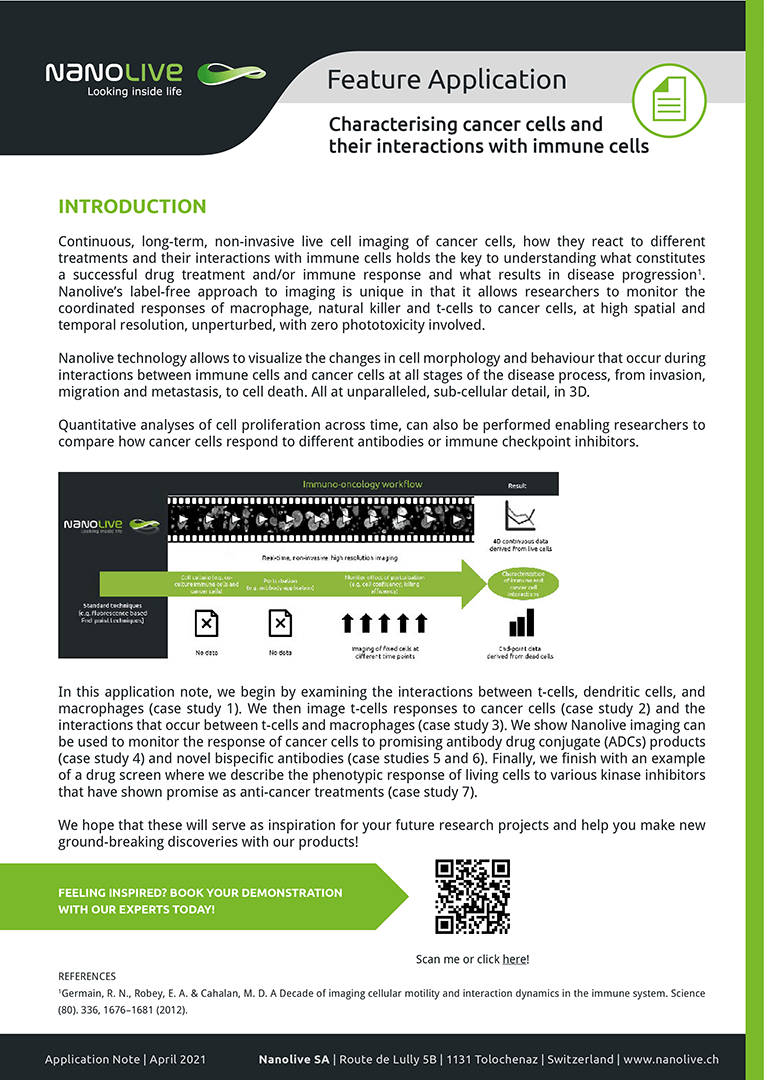
Characterizing cancer cells and their interactions with immune cells
In this application note, we begin by examining the interactions between t-cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages (case study 1). We then image t-cells responses to cancer cells (case study 2) and the interactions that occur between t-cells and macrophages (case study 3). We show Nanolive imaging can be used to monitor the response of cancer cells to promising antibody drug conjugate (ADCs) products (case study 4) and novel bispecific antibodies (case studies 5 and 6). Finally, we finish with an example of a drug screen where we describe the phenotypic response of living cells to various kinase inhibitors that have shown promise as anti-cancer treatments (case study 7).
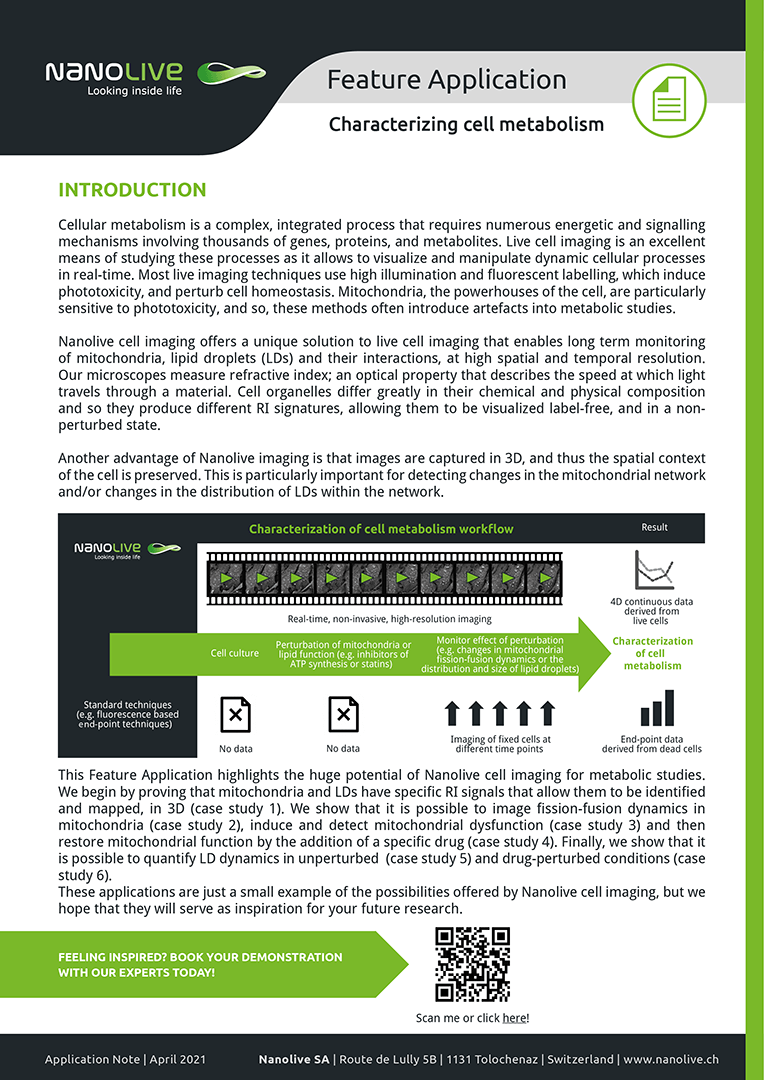
Characterizing cell metabolism
This Feature Application highlights the huge potential of Nanolive cell imaging for metabolic studies. We begin by proving that mitochondria and LDs have specific RI signals that allow them to be identified and mapped, in 3D (case study 1). We show that it is possible to image fission-fusion dynamics in mitochondria (case study 2), induce and detect mitochondrial dysfunction (case study 3) and then restore mitochondrial function by the addition of a specific drug (case study 4). Finally, we show that it is possible to quantify LD dynamics in unperturbed (case study 5) and drug-perturbed conditions (case study 6).
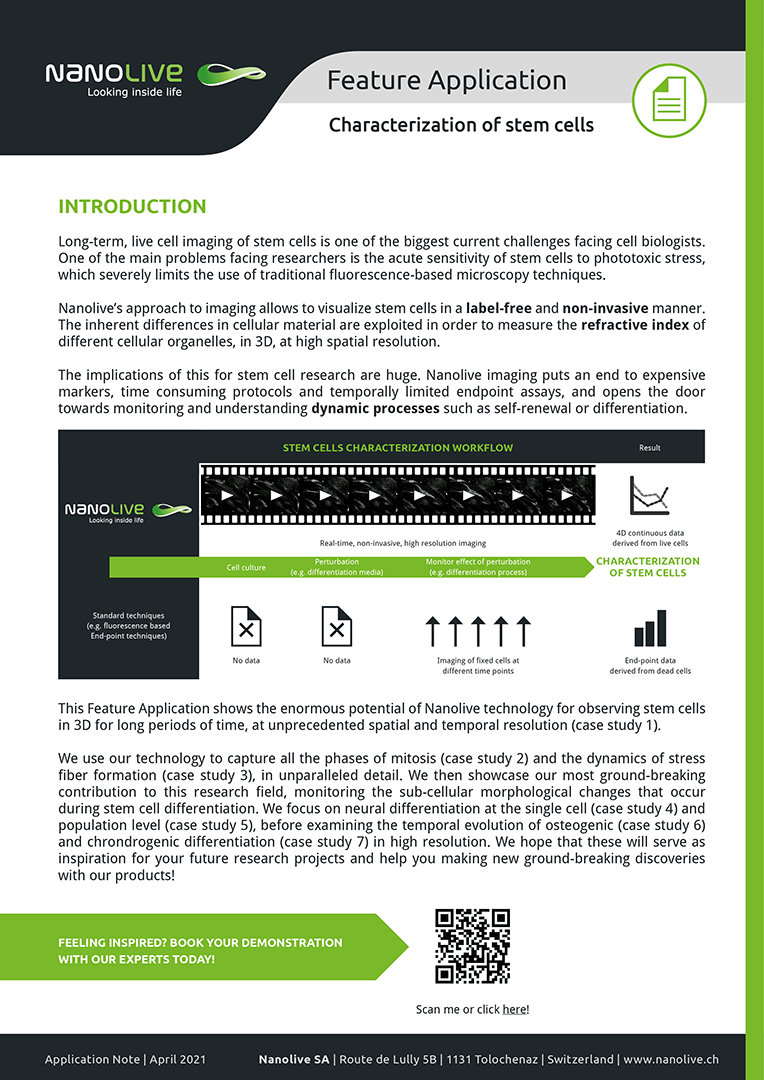
Characterizing stem cells
This Feature Application shows the enormous potential of Nanolive technology for observing stem cells in 3D for long periods of time, at unprecedented spatial and temporal resolution (case study 1). We use our technology to capture all the phases of mitosis (case study 2) and the dynamics of stress fiber formation (case study 3), in unparalleled detail. We then showcase our most ground-breaking contribution to this research field, monitoring the sub-cellular morphological changes that occur during stem cell differentiation. We focus on neural differentiation at the single cell (case study 4) and population level (case study 5), before examining the temporal evolution of osteogenic (case study 6) and chrondrogenic differentiation (case study 7) in high resolution.
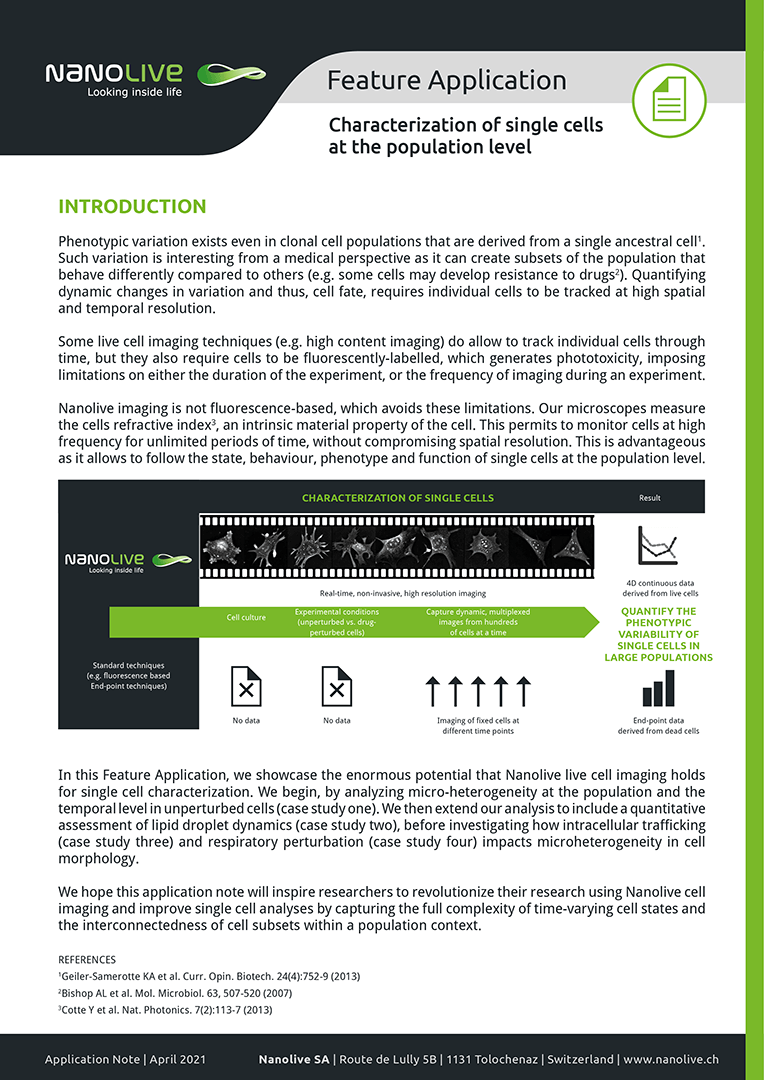
Characterizing single cells at the population level
In this Feature Application, we showcase the enormous potential that Nanolive live cell imaging holds for single cell characterization. We begin, by analyzing micro-heterogeneity at the population and the temporal level in unperturbed cells (case study one). We then extend our analysis to include a quantitative assessment of lipid droplet dynamics (case study two), before investigating how intracellular trafficking (case study three) and respiratory perturbation (case study four) impacts microheterogeneity in cell morphology.
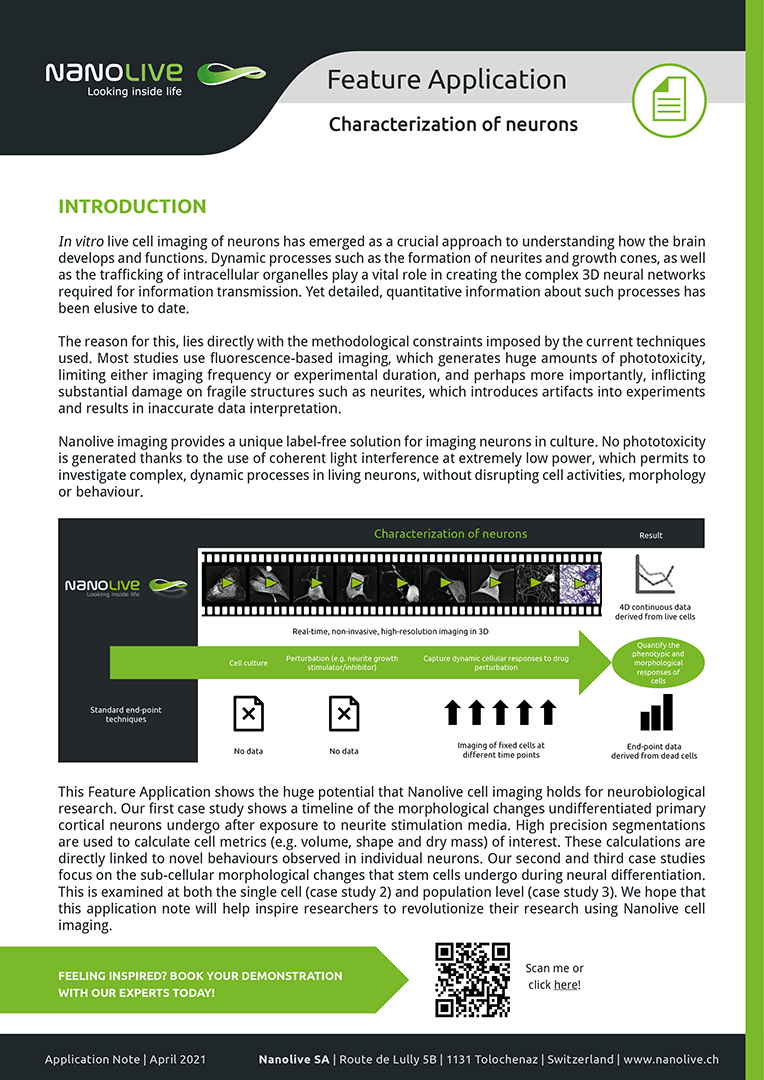
Characterizing neurons
Here, we feature a timeline of the morphological changes undifferentiated primary cortical neurons undergo after exposure to neurite stimulation media. We show how our high precision segmentations can be used to calculate cell metrics (e.g. volume, shape and dry mass) of interest and link these directly to novel behaviours observed in individual neurons (case study one). We examine the sub-cellular morphological changes that stem cells undergo during neural differentiation, at both the single cell (case study 2) and population level (case study 3).
Technical Notes
LIVE Cell Death Assay
In this Technical Note, we will explain in detail how the LCDA works and what the output is. We showcase the functioning of the product in multiple cell types and compare its performance against a standard, state-of-the-art fluorescence-based live cell imaging kit. We finish with a case study, where we use the LCDA to quantify the cell death dynamics induced by Ebastine, a drug that has shown promise in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.
Smart Lipid Droplet Assay LIVE
In this Technical Note, we introduce the Smart Lipid Droplet Assay (SLDA) and showcase its output in multiple cell types at varying confluences and across different field of view sizes. We then compare the performance of the SLDA against the fluorescence marker LipidSpot 610, before finishing with a case study where we use the SLDA to quantify how oleic acid (OA) addition changes LD dynamics in pre-adipocyte cells.
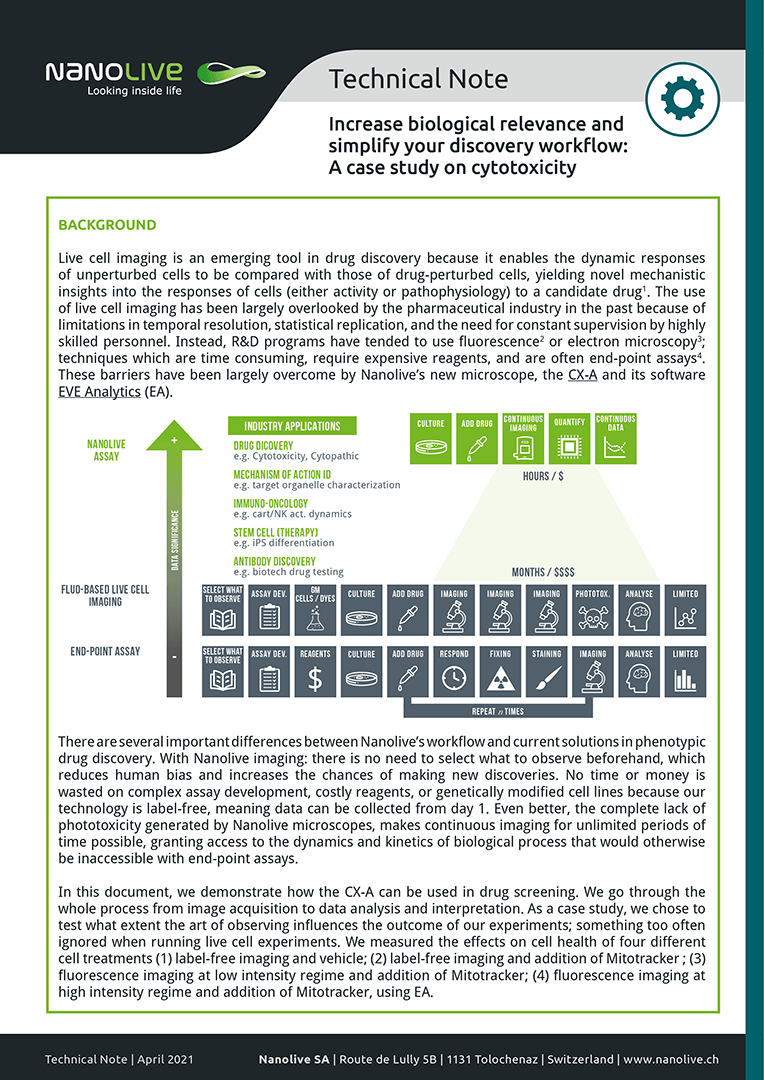
Increase biological relevance and simplify your discovery workflow
In this document, we demonstrate how the CX-A can be used in drug screening. We go through the whole process from image acquisition to data analysis and interpretation. As a case study, we chose to test what extent the art of observing influences the outcome of our experiments; something too often ignored when running live cell experiments. We measured the effects on cell health of four different cell treatments (1) label-free imaging and vehicle; (2) label-free imaging and addition of Mitotracker; (3) fluorescence imaging at low intensity regime and addition of Mitotracker; (4) fluorescence imaging at high intensity regime and addition of Mitotracker, using EA.
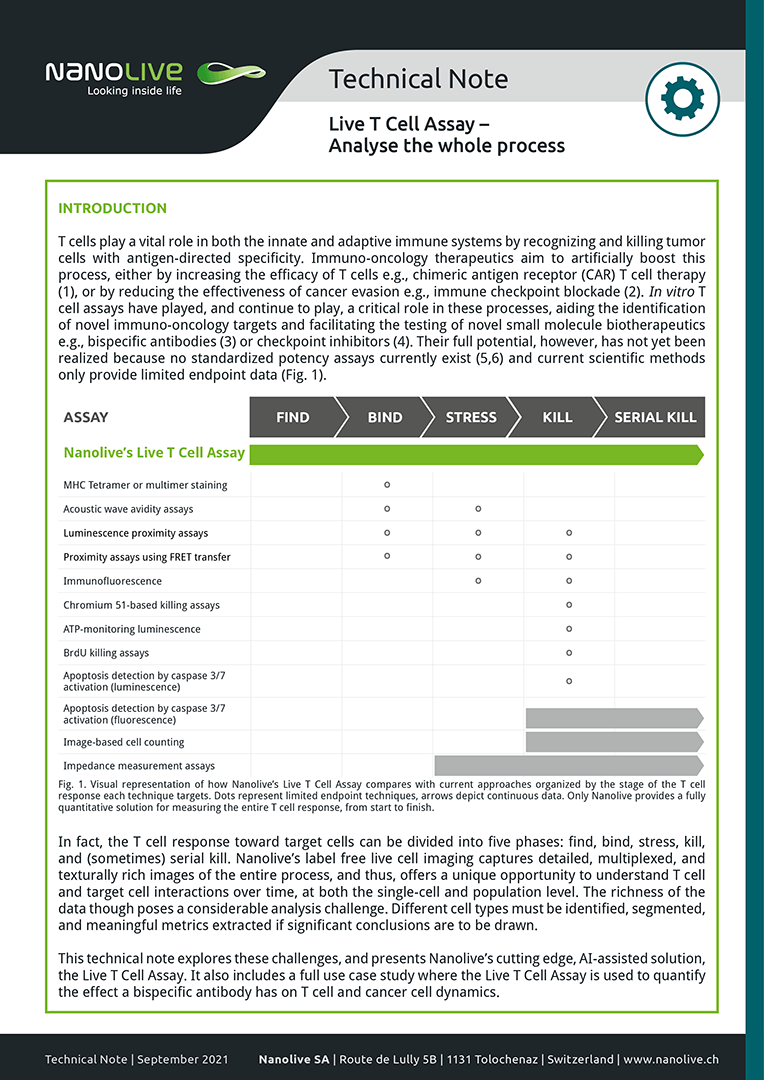
Presenting the Live T Cell Assay
This technical note explores these challenges, and presents Nanolive’s cutting edge, AI-assisted solution, the Live T Cell Assay. It also includes a full use case study where the Live T Cell Assay is used to quantify the effect a bispecific antibody has on T cell and cancer cell dynamics.
Evaluating the performance of EVE Analytics
In this technical note, we introduce the key elements involved in cell segmentation, which are essential to understand the novelty of EVE Analytics (EA), Nanolive’s software solution for quantitative cell analysis. We then evaluate the performance of EA segmentation against fluorescence-based segmentation and compare how metrics produced by both approaches differ.
Nanolive imaging and analysis platforms
Swiss high-precision imaging and analysis platforms that look instantly inside label-free living cells in 3D

3D CELL EXPLORER 96focus
Automated label-free live cell imaging and analysis solution: a unique walk-away solution for long-term live cell imaging of single cells and cell populations

3D CELL EXPLORER-fluo
Multimodal Complete Solution: combine high quality non-invasive 4D live cell imaging with fluorescence

3D CELL EXPLORER
Budget-friendly, easy-to-use, compact solution for high quality non-invasive 4D live cell imaging