The refractive index of cellular structures is an intrinsic property that is used by Nanolive’s imaging and digital assays to analyse cells and organelles label-free. The authors of a newly published paper in Cells have innovatively applied this technology to monitor changes in cancerous and healthy cells. This discovery may open the door to new diagnostic tests to detect tumour cells from a blood test in future.
In ‘Quantitative Phase Imaging Detecting the Hypoxia-Induced Patterns in Healthy and Neoplastic Human Colonic Epithelial Cells’, Professor Buzalewicz et al. used Nanolive’s label-free imaging to study cellular structures such as the cytoplasm, nucleus, and lipid droplets by their refractive index (RI) values, and to quantify their characteristics such as volume and dry mass1.
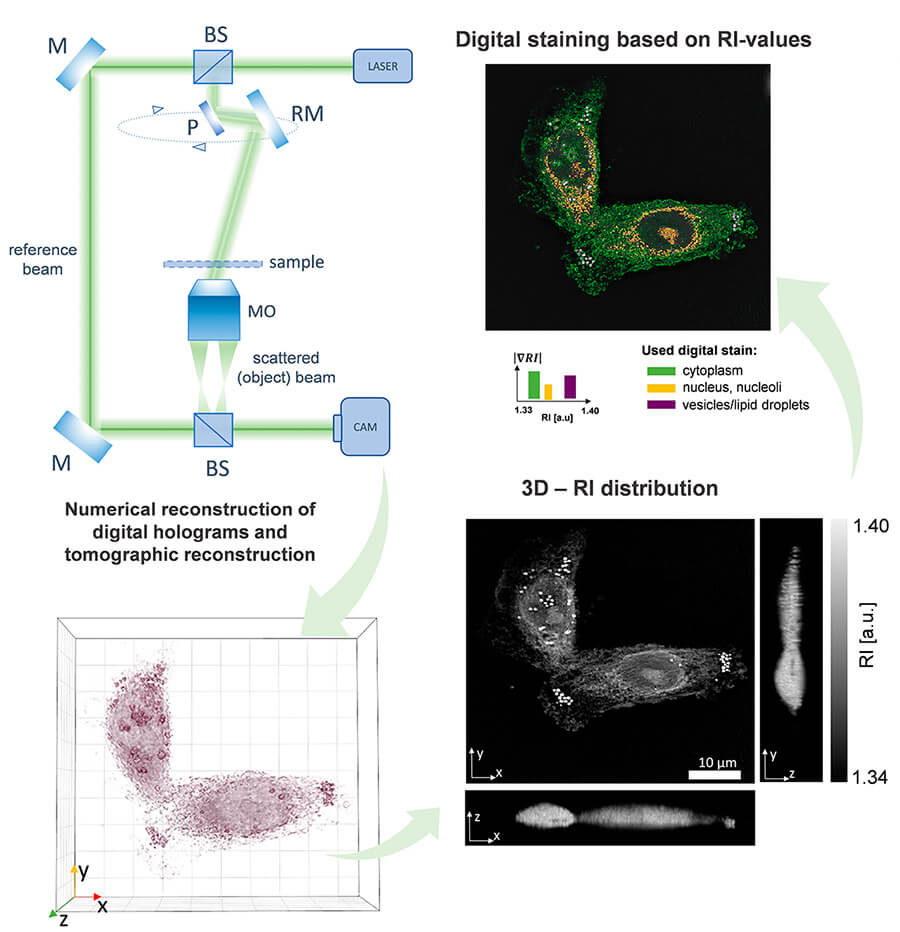
Cell imaging methodology performed using the Nanolive platform. Image modified from Figure 3, Buzalewicz, I. et al. Used with permission.
A new diagnostic test for colon cancers?
Imaging with Nanolive determined that lipid droplets increased in volume in two cancerous cell lines but did not change in the healthy cell line under hypoxic conditions; a difference that has potential for cancer cell detection.
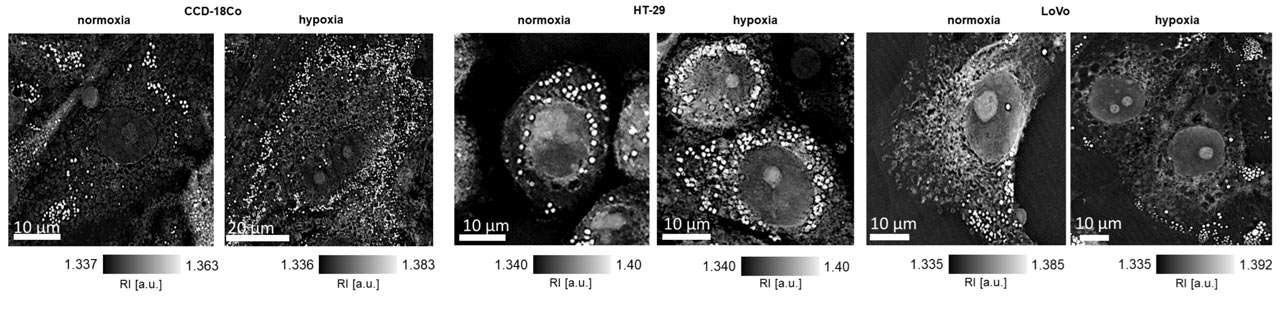
Nanolive imaging was used to detect changes in lipid droplet volume under hypoxic conditions. Image taken from Figure 5, Buzalewicz, I. et al. Used with permission.
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) with aggressive metastatic phenotypes can lose the markers currently used to detect them via immunofluorescence, necessitating another approach. As the authors noted, label-free imaging vastly speeds up the imaging process, giving more biologically relevant results earlier, and faster; “the specimens can be examined immediately after their collection at the patient’s bedside”1. After imaging with Nanolive, cells remain unfixed and unperturbed, allowing further downstream analysis as required to aid diagnosis.
We are looking forward to seeing how the authors continue to develop this idea! The full paper is available here.
“Imaging by [digital holotomography] is a quick and intuitive procedure, which with the relatively simple use of the device may bring new possibilities for the early detection of CTCs.”
Explore the role of lipid droplets in cancer with the Smart Lipid Droplet AssayLIVE
Lipid droplets are known to play key roles in many cancer cell processes, and to modulate hypoxic conditions to promote cancer cell survival2. If this paper has inspired you to look more closely into lipid droplets, we now have a digital assay to automate the detection and segmentation of lipid droplets in cells. The Smart Lipid Droplet AssayLIVE produces an expanded range of metrics including the average distance of lipid droplets to the centre of the parent cell, compactness, granularity, count and more. Metrics are available for all lipid droplets, and for lipid droplets per cell.
References:
- Buzalewicz, I., et al. Quantitative Phase Imaging Detecting the Hypoxia-Induced Patterns in Healthy and Neoplastic Human Colonic Epithelial Cells. Cells 2022, 11(22), 3599; https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223599
- Cruz, A.L.S., et al. Lipid droplets: platforms with multiple functions in cancer hallmarks. Cell Death Dis 11, 105 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2297-3
Read our latest news
Cytotoxic Drug Development Application Note
Discover how Nanolive’s LIVE Cytotoxicity Assay transforms cytotoxic drug development through high-resolution, label-free quantification of cell health and death. Our application note explores how this advanced technology enables real-time monitoring of cell death...
Investigative Toxicology Application Note
Our groundbreaking approach offers a label-free, high-content imaging solution that transforms the way cellular health, death, and phenotypic responses are monitored and quantified. Unlike traditional cytotoxicity assays, Nanolive’s technology bypasses the limitations...
Phenotypic Cell Health and Stress Application Note
Discover the advanced capabilities of Nanolive’s LIVE Cytotoxicity Assay in an application note. This document presents a detailed exploration of how our innovative, label-free technology enables researchers to monitor phenotypic changes and detect cell stress...



